The Angle: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[category: |
[[category: Characteristics_of_lighting]] |
||
== '''Introduction :'''== |
== '''Introduction :'''== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Today we will focus on the first characteristic, which is one of the more signifiant: The direction. |
|||
The angle of the main light is a huge source of meaning. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
more lighting to compose an image, to soften it (because a single lamp gives hard shadows), or to detach |
more lighting to compose an image, to soften it (because a single lamp gives hard shadows), or to detach |
||
it from the background of the theater. |
it from the background of the theater. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Little explanation... |
|||
Research : |
|||
I searched days in books and on the web material describing the semiotic aspects of the direction of the |
|||
light and here is what i found : |
|||
Very basic, nice anyway: |
|||
https://www.matrix.edu.au/film-techniques-lighting/ |
https://www.matrix.edu.au/film-techniques-lighting/ |
||
We can define and Identify the lighting elements in the scene: |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
2. Quality of lighting |
|||
3. Source of lighting |
|||
4. Colour of lighting |
|||
This website, shows and defined the 4 basic directions and the quality of the light. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Frontal lighting :It is a neutral lighting that diffuses no shadows on the face. You will find it is mostly |
'''Frontal lighting :''' It is a neutral lighting that diffuses no shadows on the face. You will find it is mostly |
||
used for portraits or to emphasise an object or subject. |
used for portraits or to emphasise an object or subject. |
||
Sidelight :Sidelight creates a shadow on one half of the subject and sculpts the subject’s features. The |
'''Sidelight :''' Sidelight creates a shadow on one half of the subject and sculpts the subject’s features. The |
||
contrast between light and shadow creates a sense of mystery |
contrast between light and shadow creates a sense of mystery |
||
Backlighting :Backlighting creates silhouettes and a glowing effect on the subject. This is used to create |
'''Backlighting :''' Backlighting creates silhouettes and a glowing effect on the subject. This is used to create |
||
a dramatic effect and emphasise the subject in a mysterious way. You may see directors use backlighting |
a dramatic effect and emphasise the subject in a mysterious way. You may see directors use backlighting |
||
to introduce a superior character without revealing their identity. |
to introduce a superior character without revealing their identity. |
||
Underlighting :Underlighting can either be used as a monumental lighting (light up a statue) or distort |
'''Underlighting :''' Underlighting can either be used as a monumental lighting (light up a statue) or distort |
||
the subject’s features (ghost stories around the campfire). It creates feelings of fear, curiosity or awe. |
the subject’s features (ghost stories around the campfire). It creates feelings of fear, curiosity or awe. |
||
Quality of lighting : |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Hard/harsh lighting :It creates a dramatic and intense atmosphere. |
Hard/harsh lighting :It creates a dramatic and intense atmosphere. |
||
Soft/diffused lighting :It creates a romantic, dreamlike or magical atmosphere. |
Soft/diffused lighting :It creates a romantic, dreamlike or magical atmosphere. |
||
== '''Semiotic concepts:''' == |
|||
Very interesting but too complexe for a first introduction : |
|||
the perception of the angle of the light is also linked with neuro-cognitive sciences : « psychology of art and the evolution of the conscious brain » by |
|||
Robert L. Solso |
Robert L. Solso. |
||
On the adaptation of semiotics to the framework of theater studies : |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Martin Esslin as Roland Barthes insist on this aspect: |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
are all systems of visual signs that constitute the foundations of any drama. " |
are all systems of visual signs that constitute the foundations of any drama. " |
||
"Theater is indeed this practice that calculates the looked place of things: if I put the show here, the |
"Theater is indeed this practice that calculates the looked place of things: if I put the show here, the |
||
spectator will see that. " |
spectator will see that. " |
||
Very strong, interesting, complicated researche on semiotic by the logician and philosopher Charles |
|||
Sanders Pierce. |
|||
A more simple, relevant and interesting way to analyse by : JACQUES LOISELEUX, La Lumière |
|||
au cinéma, Cahier du cinéma (les Petits Cahiers), SCEREN-CNDP, Paris, 2004, p3. |
|||
"[Light can] give meaning to the image by the way it illuminates the subject and by the emotion it |
|||
creates." |
|||
He speaks of three signifiers of light in cinema: one is technical, the other psychological, which |
|||
gives emotional values, and the last cultural, which appeals to the cognitive memory, the |
|||
reservoir of luminous sensations of each. |
|||
And I think it would be great to research all together on that with this simple and relevant |
|||
système. |
|||
The logician and philosopher Charles Sanders Pierce has also published a very interesting research on semiotics and the signifiers of the angle of light can be analysed in a very precise way through his study protocol. |
|||
First : a bit of vocabulary to know where we are on stage : |
|||
A simpler, relevant and interesting way of analysing it is finally defined by JACQUES LOISELEUX, La Lumière au cinéma, Cahier du cinéma (les Petits Cahiers), SCEREN-CNDP, Paris, 2004, p3. "[Light can] give meaning to the image by the way it illuminates the subject and by the emotion it arouses." |
|||
He talks about three signifiers of light in cinema: a technical signifier, a psychological signifier, which gives emotional values, and a cultural signifier, which appeals to one's cognitive memory, one's reservoir of light sensations. And I think it would be great to do research on this subject with this system. |
|||
== '''Stage vocabulary to analyse :''' == |
|||
Stage Left (Left of the performer from their perspective) |
Stage Left (Left of the performer from their perspective) |
||
Stage Right (Right of the performer from their perspective) |
Stage Right (Right of the performer from their perspective) |
||
Center (same from stage perspective and house perspective) |
Center (same from stage perspective and house perspective) |
||
Upstage (the rear of the stage, behind the performer) |
Upstage (the rear of the stage, behind the performer) |
||
Downstage (the front of the stage, closest to the audience) |
Downstage (the front of the stage, closest to the audience) |
||
Midstage (In between Upstage and Downstage) |
Midstage (In between Upstage and Downstage) |
||
Onstage and Offstage (used to direct fine adjustments, same from both house and stage |
Onstage and Offstage (used to direct fine adjustments, same from both house and stage |
||
positions) |
positions) |
||
House Left (Left from the audience perspective, usually describing something NOT on stage) |
House Left (Left from the audience perspective, usually describing something NOT on stage) |
||
House Right (Right from the audience perspective, ditto) |
House Right (Right from the audience perspective, ditto) |
||
FOH (describing the control position and/or house lighting position) |
FOH (describing the control position and/or house lighting position) |
||
== '''The experiment :''' == |
|||
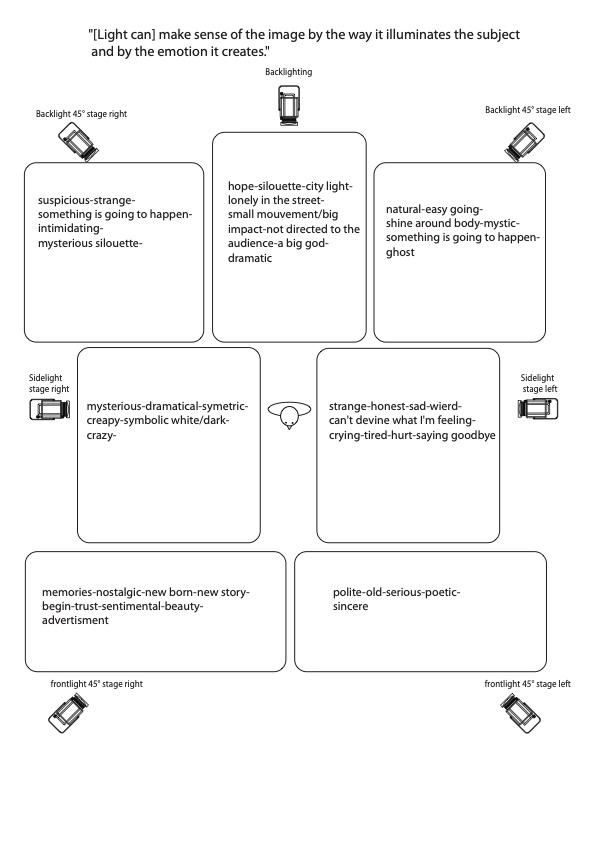
See the 2 papers with lighting angles written. |
See the 2 papers with lighting angles written. |
||
Experimentation made by university students 2nd year performence: |
|||
with somebody saying the same text, we will change the direction of the light and write what we feel. |
with somebody saying the same text, we will change the direction of the light and write what we feel. |
||
Latest revision as of 12:42, 22 December 2022
Introduction :
The angle of the main light is a huge source of meaning. It is this light that defines the direction. Very often there is more lighting to compose an image, to soften it (because a single lamp gives hard shadows), or to detach it from the background of the theater.
4 Main Directions :
https://www.matrix.edu.au/film-techniques-lighting/
This website, shows and defined the 4 basic directions and the quality of the light.
Frontal lighting : It is a neutral lighting that diffuses no shadows on the face. You will find it is mostly used for portraits or to emphasise an object or subject.
Sidelight : Sidelight creates a shadow on one half of the subject and sculpts the subject’s features. The contrast between light and shadow creates a sense of mystery
Backlighting : Backlighting creates silhouettes and a glowing effect on the subject. This is used to create a dramatic effect and emphasise the subject in a mysterious way. You may see directors use backlighting to introduce a superior character without revealing their identity.
Underlighting : Underlighting can either be used as a monumental lighting (light up a statue) or distort the subject’s features (ghost stories around the campfire). It creates feelings of fear, curiosity or awe.
Quality of lighting : Hard/harsh lighting :It creates a dramatic and intense atmosphere.
Soft/diffused lighting :It creates a romantic, dreamlike or magical atmosphere.
Semiotic concepts:
the perception of the angle of the light is also linked with neuro-cognitive sciences : « psychology of art and the evolution of the conscious brain » by Robert L. Solso.
Both Martin Esslin and Roland Barthes insist on the relevance of researching the adaptation of semiotics in theatre studies: "The architectural setting of a performance, the actors and their actions, the sets, costumes, and lighting are all systems of visual signs that constitute the foundations of any drama. " "Theater is indeed this practice that calculates the looked place of things: if I put the show here, the spectator will see that. "
The logician and philosopher Charles Sanders Pierce has also published a very interesting research on semiotics and the signifiers of the angle of light can be analysed in a very precise way through his study protocol.
A simpler, relevant and interesting way of analysing it is finally defined by JACQUES LOISELEUX, La Lumière au cinéma, Cahier du cinéma (les Petits Cahiers), SCEREN-CNDP, Paris, 2004, p3. "[Light can] give meaning to the image by the way it illuminates the subject and by the emotion it arouses."
He talks about three signifiers of light in cinema: a technical signifier, a psychological signifier, which gives emotional values, and a cultural signifier, which appeals to one's cognitive memory, one's reservoir of light sensations. And I think it would be great to do research on this subject with this system.
Stage vocabulary to analyse :
Stage Left (Left of the performer from their perspective)
Stage Right (Right of the performer from their perspective)
Center (same from stage perspective and house perspective)
Upstage (the rear of the stage, behind the performer)
Downstage (the front of the stage, closest to the audience)
Midstage (In between Upstage and Downstage)
Onstage and Offstage (used to direct fine adjustments, same from both house and stage positions)
House Left (Left from the audience perspective, usually describing something NOT on stage)
House Right (Right from the audience perspective, ditto)
FOH (describing the control position and/or house lighting position)
The experiment :
See the 2 papers with lighting angles written.
Experimentation made by university students 2nd year performence:
with somebody saying the same text, we will change the direction of the light and write what we feel.